Trigonometric functions
Trigonometric functions
Unit Circle radius is 1 (Unity):
Before we dive into the trigonometric functions, it is understood that the student already knows the following:
-Basic knowledge of similar triangles.
-Definition of circle.
-Meaning of a function
The Unit circle is a circle of radius 1 (unity). Angles are counted counterclockwise from 0 to 360 degrees where 360 degrees is 0 again.
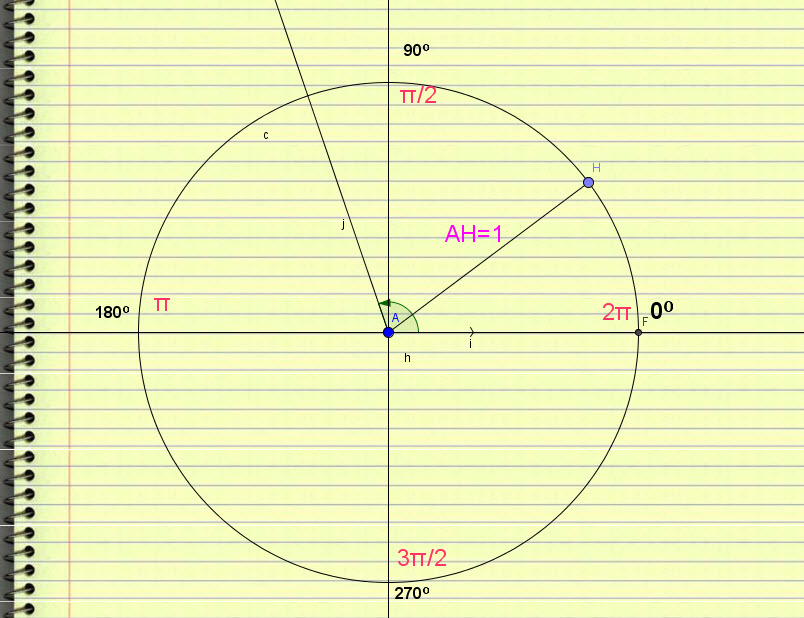
As we can see in the figure, we start at 0 degrees which is also 360 degrees or 2π.
When we reach 90 degrees we have π/2 and so on…
This gives us a solid ground for the trigonometric functions studies.
We see above some equivalence that will have an impact in future:
π radians = 180 degrees
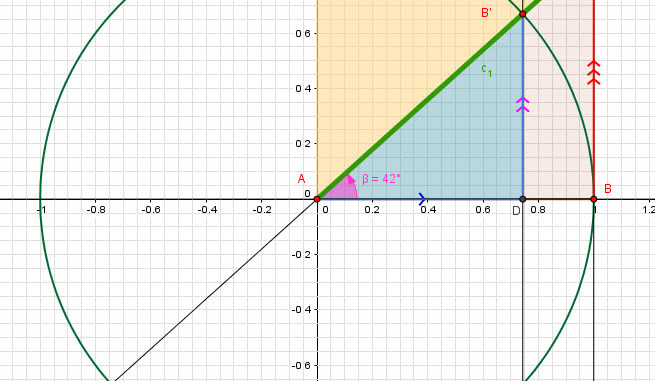
The SINE of an angle:
If you look from the center of the circle, the vertical line FB’ is the Sine of angle BAB’
Please note that this is true only because AB’=1 (the radius).
The sine takes the sign of the y-coordinate.
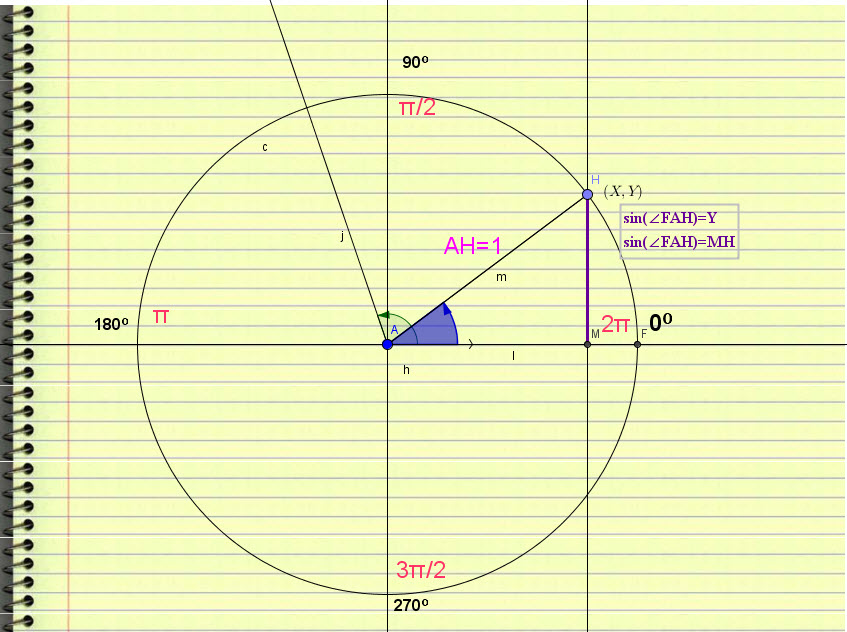
-It is obvious that if we keep changing the angle, the SINE changes from 0 (at 0 degrees) to 1 at 90 degrees, then to 0 again at 180 degrees before starting to become <0 and reach -1 at 270 degrees just to return to the starting value at 0.
What we learned about sin(α):
-Its maximum is 1.
-its minimum is -1.
When we calculate sin(α) we never go beyond these values.
In any situation, if we get a radius of 1, we’ll come to that later, we have the sine function of the angle.
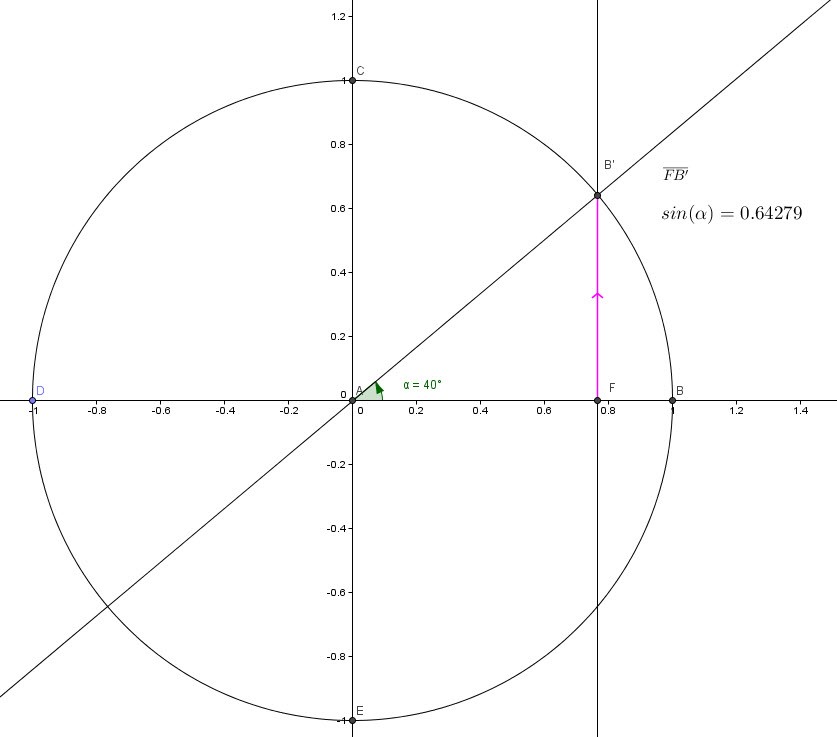
This was a quick introduction to the sine function.


Be the first to comment