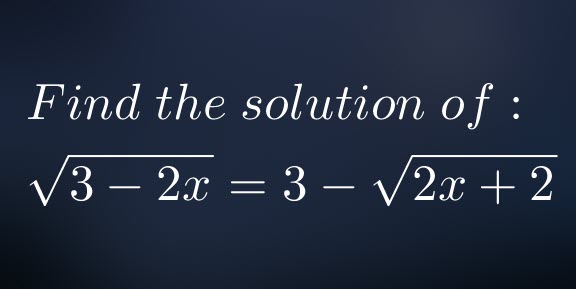
Find the solution of:![]()
Solution:![]()
Let’s square the two sides:
We get:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Adding similar terms we get:![]()
![]()
Multiplying both sides by ![]()
![]()
Let’s square both sides another time:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Divide by 2:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let’s factor:![]()
![]()
![]()
The equality is true if any factor is zero.![]()
The same way:![]()
If we plugin we verify that both roots are valid:
Finally:
The solution set is:
![]()


Be the first to comment